When I inherited my grandfather’s old tools, they were scattered in a worn-out biscuit tin. Over the years, I realized that a well-organized toolbox stocked with basic hand tools is crucial for tackling home repairs, woodworking projects, and even metalworking. So, I decided to upgrade to a sturdy wooden toolbox, and it transformed my DIY projects.
We’ll walk you through the basic hand tools list that every homeowner, DIY enthusiast, or beginner should have. From hammers to measuring tools, we have everything you need to know to build a functional and efficient toolbox.
Hammers: Tools of Force
Hammers are versatile tools used in countless applications, from construction to metalworking. They come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks.
Common Types of Hammers
- Claw Hammer: This is the most common type, featuring a curved claw for removing nails. striking face is typically flat.
- Ball Peen Hammer: This hammer has a rounded, striking face, ideal for shaping metal and driving in pins or rivets.
- Sledge Hammer: This heavy-duty hammer is used for demolition and other tasks requiring significant force. It has a large, flat striking face.
Key Features of Hammers
- Striking face: The part that comes into contact with the material being struck.
- Handle: The part you hold to apply force. Anti-shock handles help reduce vibration and fatigue.
- Claw: The curved part used for removing nails. Straight claws are more suitable for demolition work.
Applications of Hammers
- Construction: Driving nails, framing, demolition
- Metalworking: Shaping metal, riveting, forging
- Blacksmithing: Shaping metal into various forms
- Home improvement: Hanging shelves, repairing furniture
Additional Features
- Magnetic nail holders: Some hammers have built-in magnets to hold nails in place.
- Side-mounted nail pullers: These can help remove nails in tight spaces.
Remember: Always use a suitable hammer to ensure safety and efficiency.
Clamps and Pry Bars: Essential Tools for Holding and Prying
Clamps and pry bars are versatile tools used in various construction and home improvement tasks. Clamps hold materials in place, while pry bars are used for prying and demolition.
Clamps
Clamps securely hold materials together while gluing, assembling, or working on them. They come in various sizes and styles, each designed for specific applications.
- C-clamps are standard clamps with a C-shaped frame and a movable jaw. They are suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Bar clamps: These clamps have two parallel bars with adjustable jaws. They are often used for holding large or long pieces of material.
- Spring clamps: These clamps have a spring-loaded mechanism that allows them to be quickly attached and released. They are ideal for holding smaller items.
- Pipe clamps: These clamps are designed to hold pipes and other round objects.
Applications of Clamps
- Gluing applications: Clamps are essential for holding materials together while the glue dries.
- Assembling furniture: They are used to hold joints together while screws or nails are driven.
- Construction: Clamps hold studs, joists, and other building materials in place.
- Temporary vice: Clamps can be used to hold small objects while working on them.
Pry Bars
Pry bars are used to pry materials apart or lever them into place. They are often used for demolition tasks, such as removing floorboards or window frames.
- Wrecking bar: A heavy-duty pry bar with a flat tip and a curved handle.
- Floorboard pry bar: A specialized pry bar with a curved tip and a serrated edge designed for removing floorboards.
Applications of Pry Bars
- Demolition: Pry bars are used to remove nails, screws, and other fasteners.
- Prying apart materials: They can be used to separate stuck or glued materials.
- Tight spaces: Pry bars can be used to reach into tight spaces and lever objects into place.
Hand Saws: Precision Cutting Tools
Hand saws are essential tools for making precise cuts in various materials. They come in different shapes and sizes, each designed for a specific purpose.
Common Types of Hand Saws
- Hand Saw: This is the most basic type, featuring a long, rigid blade with a handle on one end. It’s used for cutting wood and other materials.
- Hacksaw: This saw has a thin, rigid blade with fine teeth, making it ideal for cutting metal. It often has a frame that allows for adjustable blade tension.
- Plasterboard Jab Saw: Designed for cutting drywall, this saw has a short, rigid blade with a pointed tip for starting cuts.
- Keyhole Saw: This saw has a narrow blade with a pointed tip, allowing you to cut holes in walls or other materials.
- Pad Saw: This saw has a small, circular blade mounted on a pad, making it suitable for cutting curves and intricate shapes.
Key Features of Hand Saws
- Blade: The main cutting element.
- Teeth: The sharp edges that cut into the material.
- Handle: The part you hold to apply force.
- Frame (for hacksaws): A metal frame that holds the blade in place.
Applications of Hand Saws
- Woodworking: Cutting lumber, framing, and making furniture
- Metalworking: Cutting metal pipes, rods, and sheets
- Construction: Cutting drywall, plaster, and other building materials
- Home improvement: Cutting wood for repairs or projects
Additional Features
- Induction-hardened teeth: Teeth that are hardened using an induction heating process for increased durability.
- Triple ground teeth: Teeth that are ground three times for a sharper and more efficient cut.
- Rasping holes: Holes in the blade that help remove material more quickly.
- Plunge tip: A pointed tip on some saws that allows you to start cutting without drilling a pilot hole.
Remember: Always use the right saw to ensure safety and efficiency.
Screwdrivers: The Essential Tool for Screws
Screwdrivers are indispensable tools for driving or removing screws. They come in various shapes and sizes, each designed to fit specific screw head types.
Common Types of Screwdrivers
- Flat Head Screwdriver: This has a flat, slotted blade that fits into slotted screw heads.
- Phillips Screwdriver: This has a cross-shaped tip that fits into Phillips screw heads.
- Torx Screwdriver: This has a star-shaped tip that fits into Torx screw heads.
- Pozi Screwdriver: This has a cross-shaped tip with a slight chamfer, designed to prevent the tip from slipping out of the screw head.
- Chisel-Driver Screwdrivers: These have a flat blade with a chisel-shaped tip, often used for slotted screws in tight spaces.
- Insulated VDE Screwdrivers: These have insulated handles for safety when working with electrical equipment.
- Ratcheting Screwdriver: This has a built-in ratchet mechanism that allows continuous turning without repositioning the screwdriver.
- Interchangeable Screwdriver Sets: These sets include multiple interchangeable blades, allowing you to have a variety of screw head types in one tool.
Key Features of Screwdrivers
- Blade: The part that fits into the screw head.
- Handle: The part you hold to apply force.
- Tip: The end of the blade that fits into the screw head.
- Torque Transfer: The ability of the screwdriver to transfer force to the screw.
Applications of Screwdrivers
- Assembly: Driving screws to assemble furniture, electronics, and other products.
- Repairs: Removing and replacing screws during repairs.
- Construction: Driving screws for various construction tasks.
- DIY Projects: Using screws for various home improvement projects.
Remember: Always use the correct screwdriver for the screw head type to avoid damaging the screw or the screwdriver. If you damage the screw, you may click on the below link to order a a kit to extract the damaged screws.
Click here to order the damaged screw extraction kit
Wrenches: Essential Tools for Turning Nuts and Bolts
Wrenches are indispensable tools for turning nuts and bolts. They come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications.
Common Types of Wrenches
- Open-End Wrench: This type of wrench has two open ends, each with a different size, making it suitable for various fastener sizes.
- Box End Wrench: This wrench has a closed loop at both ends, providing a better grip on nuts and bolts. Box end wrenches are often available in 6-point and 12-point configurations.
- Adjustable Wrench: This wrench has a movable jaw that can be adjusted to fit different fastener sizes. It’s a versatile tool but may not provide as secure a grip as fixed-size wrenches.
Key Features of Wrenches
- U-shaped jaws: The two open ends of the wrench.
- Fastener sizes: The specific sizes of nuts and bolts that the wrench can fit.
- 6-point and 12-point configurations: The number of sides on the box end of the wrench.
Applications of Wrenches
- Automotive repairs: Wrenches are essential for repairing and maintaining vehicles.
- Construction: They are used in various construction tasks, such as assembling and installing equipment.
- Machinery maintenance: Wrenches are used to maintain and repair machinery.
- Plumbing: They are used in plumbing tasks, such as installing pipes and fixtures.
Tips for Using Wrenches
- Choose the right size: Ensure the wrench fits the nut or bolt snugly to avoid slipping.
- Apply the proper force: Avoid overtightening, which can damage the fasteners or the wrench.
- Use a wrench extension if necessary: A wrench extension can provide additional reach for hard-to-reach fasteners.
Remember: Wrenches are versatile tools essential for a wide range of tasks. You can choose the correct wrench for any job by understanding the different types and their applications.
Pliers: Essential Gripping and Cutting Tools
Pliers are versatile tools for gripping, cutting, and bending various materials. They come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications.
Common Types of Pliers
- Combination Pliers: These are the most common type, featuring both a gripping jaw and a cutting edge. They are suitable for a wide range of tasks.
- Long Round Nose Pliers: These pliers have long, round jaws that are perfect for bending and twisting wires.
- Diagonal Side Cutters: These pliers have angled cutting edges that are designed for cutting wire and small metal objects.
- Needle Nose Pliers: These pliers have long, thin jaws perfect for reaching into tight spaces and gripping small objects.
- Channel Lock Pliers: These adjustable pliers have wide jaws that can be adjusted to fit different sizes of objects.
channel lock pliers - VDE Insulated Pliers: These pliers have insulated handles that protect the user from electrical shock. They are essential for working with electrical equipment.
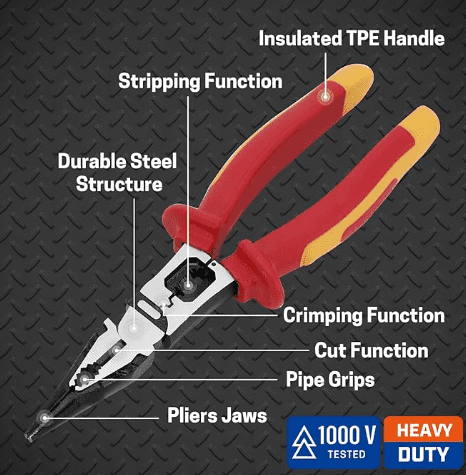
Key Features of Pliers
- Gripping jaws: The part that grips or holds objects.
- Cutting edges: The part that cuts material.
- Pivot point: The point where the two jaws meet.
- Serrated teeth: Teeth on the gripping jaws that provide extra grip.
Applications of Pliers
- Electrical work: Gripping and cutting wires, stripping insulation.
- Mechanical repairs: Gripping and turning nuts and bolts, bending and twisting metal.
- DIY projects: Assembling furniture, repairing appliances, and other tasks.
Tips for Using Pliers
- Choose the proper pliers for the job: The type of pliers you use will depend on your task.
- Apply the proper force: Avoid overtightening or overcutting, as this can damage the pliers or the material you are working with.
- Maintain your pliers: Keep them clean and lubricated to ensure they function properly.
Remember: Pliers are a versatile tool used in various applications. By understanding the different types and their features, you can choose the right pliers for any job.
Smoothing Files: Refining Rough Edges
Smoothing files, bastard files, or mill files are essential tools for removing material and smoothing rough edges on metal and other materials. They come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications.
Common Types of Smoothing Files
- Flat File: This is the most common type of smoothing file, with a flat, rectangular shape. It’s used for general smoothing and filing tasks.
- Half-Round File: This file has a flat side and another rounded side, making it versatile for flat and curved surfaces.
- Round File: This file has a round cross-section, which is ideal for smoothing round surfaces and creating holes.
- Square File: This file has a square cross-section, used for smoothing square edges and corners.
- Triangle File: This file has a triangular cross-section, often used for reaching into tight spaces and filing angles.
Key Features of Smoothing Files
- Cut: The pattern of teeth on the file. Typical cuts include bastard (coarse), second cut (medium), and dead smooth (fine).
- Shape: The overall shape of the file.
- Size: The length and width of the file.
Applications of Smoothing Files
- Metalworking: Smoothing rough edges on metal parts, filing down burrs, and creating chamfers.
- Woodworking: Smoothing rough edges on wood, shaping curves, and creating dovetails.
- Model making: Smoothing and shaping plastic and metal models.
- Repair work: Removing rust or corrosion from metal surfaces.
Tips for Using Smoothing Files
- Choose the right file: Select a file with the appropriate cut and shape for your task.
- Use the correct technique: Apply firm, even pressure, and move the file back and forth.
- Avoid excessive force: Excessive force can damage the file or the material being worked on.
- Keep the file clean: Remove metal filings from it regularly to maintain effectiveness.
Measuring and Marking Tools: Precision in Every Project
Measuring and marking tools are essential for any project that requires precision. Whether you’re building a piece of furniture, remodeling a room, or simply hanging a picture, these tools help ensure accuracy and consistency.
Common Measuring and Marking Tools
- Tape Measure: This versatile tool is used to measure lengths and distances. They come in various lengths and widths, and may feature imperial or metric scales.
- Spirit Level: This tool is used to ensure surfaces are level. It typically has a glass tube filled with a liquid, with a bubble that indicates when the surface is level.
- Carpenter’s Pencil: This specialized pencil is designed for writing on wood and other materials. It has a hard, sharp point that can make fine lines.
- Combination Square: This tool combines a square and a ruler, making it useful for measuring angles, lengths, and drawing lines.
- Stanley Tape Measures: A popular brand of tape measures known for their quality and durability.

6. Swanson Speed Square: A versatile combination square that is often used in construction and woodworking.

Key Features of Measuring and Marking Tools
- Accuracy: The ability to provide precise measurements.
- Durability: The ability to withstand wear and tear.
- Ease of use: The tool should be easy to handle and read.
- Scale: The units of measurement (imperial or metric).
Applications of Measuring and Marking Tools
- Construction: Measuring and marking lumber, framing, and other building materials.
- Woodworking: Measuring and marking wood for furniture, cabinets, and other projects.
- Home improvement: Measuring and marking for hanging shelves, installing flooring, and other tasks.
- DIY projects: Measuring and marking materials for various crafts and hobbies.
Tips for Using Measuring and Marking Tools
- Ensure accuracy: Double-check measurements to avoid errors.
- Use the right tool for the job: Choose the appropriate tool based on the task.
- Keep tools organized: Store them in a tool belt or on a workbench to keep them easily accessible.
Remember: Precision in measuring and marking is essential for successful projects. By understanding the different tools and their applications, you can ensure your work is accurate and professional.
Hex Keys: The Versatile Allen Wrench
Hex keys, also known as Allen wrenches, are essential tools for driving bolts and screws with hexagonal sockets. They are available in a variety of sizes and styles, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Types of Hex Keys
- Standard and metric sets: Most sets include standard (SAE) and metric sizes to accommodate various applications.

- Ball end: Some hex keys have a ball-shaped end, allowing for easier access to recessed screws and bolts.

- Freebie hex keys: These are often included with furniture or other products. While they may be convenient, they are generally less durable or precise than higher-quality sets.
Applications of Hex Keys
- Assembly: Hex keys are commonly used in assembly tasks, such as putting together furniture, bicycles, or electronic devices.
- General upkeep: They are also essential for maintenance and repairs, including tightening loose screws and bolts.
- Homeowner: Hex keys are a valuable tool for homeowners, as they can be used for various tasks around the house.
Choosing the Right Hex Key
- Size: Ensure that the hex key matches the size of the socket on the bolt or screw.
- Quality: High-quality hex keys will be more durable and precise than lower-quality options.
Tips for Using Hex Keys
- Apply the right amount of force: Avoid overtightening, as this can damage the threads.
- Use a wrench or pliers if necessary: For stubborn bolts or screws, a wrench or pliers can provide additional leverage.
Remember: Hex keys are a versatile tool that can be used in a variety of applications. By understanding the different types and sizes, you can choose the right hex key for any job.
Utility Knives: Versatile Cutting Tools
Utility knives are essential tools for a variety of cutting and trimming tasks. They are characterized by their retractable blades, which can be extended and retracted for safety and convenience.
Types of Utility Knives
- Folding Utility Knives: These knives have a folding mechanism that allows the blade to be retracted into the handle when not in use.
- Retractable Blade Utility Knives: These knives have a retractable blade that can be extended and retracted with a push of a button.
- Fixed Blade Utility Knives: These knives have a blade that is permanently attached to the handle. While they are less portable, they can offer better control and durability.
Key Features of Utility Knives
- Retractable blade: A blade that can be extended and retracted for safety and convenience.
- Cutting edges: The sharp edges of the blade that are used for cutting.
- Replaceable blades: Many utility knives have replaceable blades, which can be easily swapped out when they become dull.
- Hardening process: The process of making the blade harder and more durable.
Applications of Utility Knives
- Cutting cables: Utility knives can be used to cut various cables, including electrical and coaxial cables.
- Score plasterboard: They can be used to score plasterboard before breaking it along the scored line.
- Sharpen pencils: A utility knife can be used to sharpen pencils when a pencil sharpener is unavailable.
- General cutting tasks: Utility knives are versatile tools that can be used for a wide range of cutting tasks, such as trimming cardboard, cutting fabric, and opening packages.
Always use a utility knife cautiously and follow safety guidelines to prevent injuries.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Hand Tool Safety
When using hand tools, it’s essential to prioritize safety to prevent injuries. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) safeguards workers from potential hazards.
Standard PPE for Hand Tool Tasks
- Gloves: Protect hands from cuts, abrasions, and chemical exposure. Choose gloves suitable for the specific task, such as leather gloves for gripping and cutting or nitrile gloves for chemical handling.

2. Safety Glasses: Shield eyes from flying debris, dust, and chemicals. Safety glasses should fit snugly and provide adequate protection.

3. Hearing Protection: Protect ears from excessive noise, especially when using power tools or working in noisy environments. Earplugs or earmuffs are effective options.
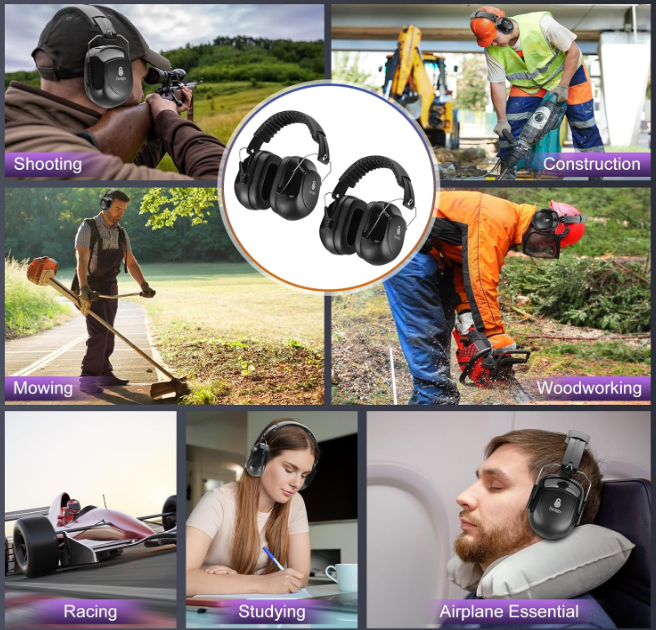

4. Respiratory Protection: Protect lungs from airborne particles, dust, and fumes. Masks or respirators are necessary when working with hazardous materials.

5. Footwear: Wear sturdy, closed-toe shoes to protect feet from falling objects and potential hazards on the job site. Safety boots with steel-toed protection are ideal.

6. Chaps: Chaps protect legs from cuts and injuries when working with chainsaws.

Importance of PPE
- Reduces injury risk: PPE can prevent or minimize injuries caused by accidents, exposure to hazardous materials, or repetitive tasks.
- Enhances safety: PPE creates a safer working environment for both the individual and others on the job site.
- Complies with regulations: Many industries and workplaces have specific PPE requirements that must be followed.
Tips for Using PPE
- Choose the right PPE: Select appropriate equipment for the task and fits properly.
- Inspect regularly: Check PPE for damage or wear before each use.
- Store properly: Store PPE in a clean, dry place to maintain its effectiveness.
- Use as intended: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use.
By prioritizing PPE and using it correctly, you can significantly reduce the risk of injuries and create a safer working environment.
Organizing Your Toolbox
Having the right tools is essential, but keeping them organized is equally crucial. A cluttered toolbox makes finding the tools you need harder, leading to frustration and wasted time. Use a toolbox with compartments to keep everything in its place, and regularly clean and maintain your tools to extend their lifespan.


























