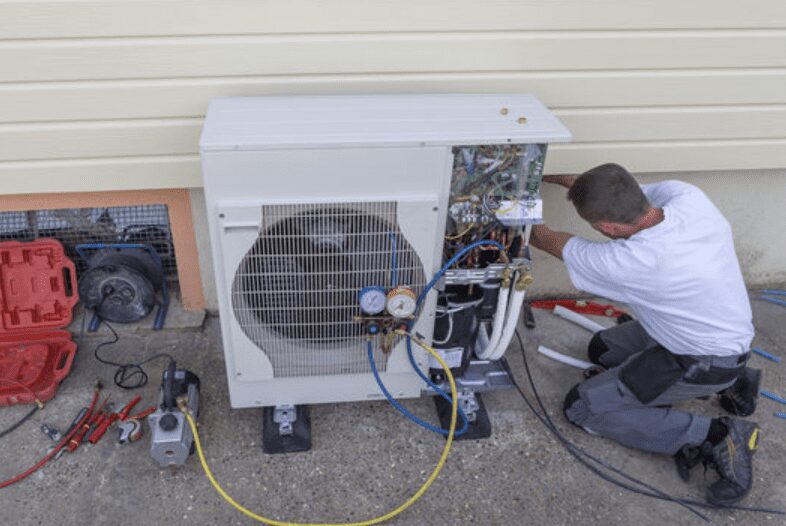
Explore the advantages of heat pump installation in your home with our in-depth guide. Dive into different heat pump varieties, cost evaluations, upkeep essentials, and more. Enhance your home’s heating and cooling capabilities for superior energy efficiency and ultimate comfort.
Heat pumps are innovative and energy-efficient devices that provide heating and cooling for residential and commercial spaces. Heat pumps deliver comfortable indoor temperatures by harnessing renewable energy from the surrounding environment while significantly reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Understanding Heat Pumps
The quest for energy-efficient and sustainable heating and cooling solutions is becoming increasingly important as homeowners and businesses strive to reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills.
Heat pumps, which harness renewable energy from the environment, are innovative and energy-efficient devices that provide comfortable indoor temperatures all year round.
Heat Pump Basics
The science behind heat pumps
Heat pumps transfer heat from one location to another, using a refrigerant as the medium for heat exchange. In heating mode, a heat pump absorbs heat from the outside air, the ground, or a water source and transfers it indoors.
In cooling mode, the process is reversed, with the heat pump extracting heat from the indoor air and releasing it outside. This heat transfer process is made possible by the refrigeration cycle, which involves the continuous circulation of refrigerant through various components.
Components and operation
A typical heat pump system comprises an outdoor unit (compressor and condenser), an indoor unit (evaporator and air handler), refrigerant lines, and a thermostat or control system.
The key components work together continuously to move heat from one location to another, providing efficient heating and cooling for your space.
The refrigeration cycle: Heating and cooling modes
The refrigeration cycle is the heart of the heat pump’s operation. In heating mode, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the outdoor environment as it evaporates in the outdoor unit. The refrigerant then travels through the refrigerant lines to the indoor unit, where it releases heat as it condenses.
This process effectively warms indoor air. In cooling mode, the cycle is reversed, with the refrigerant absorbing heat from the indoor air and releasing it outdoors.
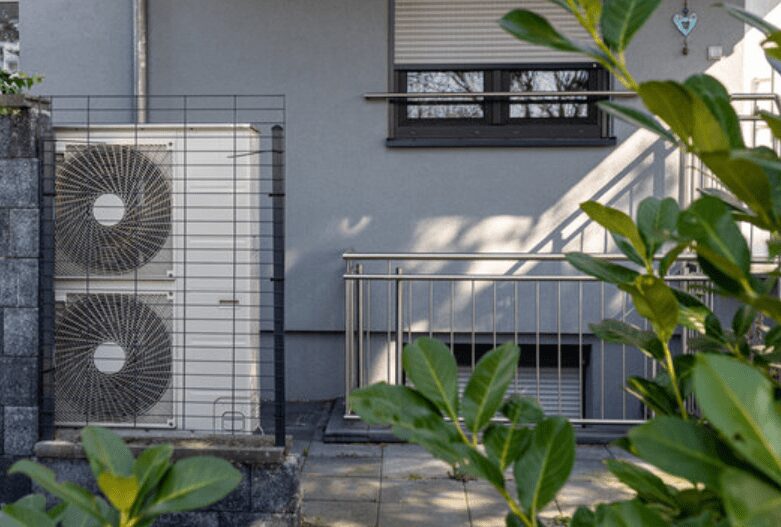

Types of Heat Pumps
Air source heat pumps
Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) are the most common type of heat pump and work by extracting heat from the outdoor air. They are relatively easy to install and suitable for various climates, although their efficiency may decrease in freezing temperatures.
Ground source (geothermal) heat pumps
Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs), also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilize the ground’s or groundwater’s stable temperatures to provide heating and cooling. While more expensive to install than ASHPs, they offer higher efficiency and are unaffected by outdoor air temperatures.
Water source heat pumps
Water source heat pumps use a body of water, such as a pond or lake, as a heat exchange medium. These systems are less common than air-source and ground-source heat pumps but can provide efficient heating and cooling in suitable locations.
Hybrid heat pumps
Hybrid heat pumps combine the features of air source and ground source systems, offering enhanced efficiency and versatility. They can automatically switch between different heat exchange sources depending on the outdoor conditions, maximizing energy savings.
Benefits of Heat Pumps
Energy efficiency and cost savings
Heat pumps can provide up to three times more heat energy than the electricity consumed, making them highly energy-efficient. This translates to significant cost savings on energy bills and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Environmental advantages
Heat pumps contribute to a lower carbon footprint and a more sustainable future by harnessing renewable energy sources and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Versatility and year-round comfort
Heat pumps offer heating and cooling functions, providing consistent comfort throughout the year. With a single system, homeowners and businesses can maintain optimal indoor temperatures in all seasons.
Low maintenance requirements
Compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, heat pumps require less maintenance. Periodic cleaning of filters, coils, and fans and an annual professional inspection is generally sufficient to keep the system running efficiently.
Applications of Heat Pumps
Residential heating and cooling
Heat pumps are an excellent choice for homeowners looking to upgrade their existing HVAC systems or install new heating and cooling solutions. With various types and sizes available, there’s a heat pump to suit the needs of any home, from small apartments to large houses.
Commercial and industrial settings
Heat pumps are also increasingly popular in commercial and industrial buildings, offering energy-efficient climate control for offices, retail spaces, warehouses, and more. In addition to heating and cooling, heat pumps can be integrated with other systems, such as heat pump water heaters and radiant floor heating, to enhance their performance and energy savings further.
Integration with existing HVAC systems
For those with existing HVAC systems, heat pumps can often be integrated seamlessly, either as a supplement to the current system or as a replacement for older, less efficient equipment. This integration can help improve overall energy efficiency and reduce operating costs.
Assessing Your Home
Before installing a heat pump, assessing your home must ensure you choose the right system. Factors such as climate, insulation, and energy efficiency are critical in determining your home’s most suitable heat pump. Proper heat pump sizing is also essential to optimize performance and energy savings.
Climate considerations
The climate in your area significantly impacts the type and efficiency of the heat pump you should choose. While air-source heat pumps suit most environments, their efficiency decreases in frigid temperatures.
Ground source or geothermal heat pumps may be a better option in colder regions due to their stable performance, regardless of outdoor air temperatures. Conversely, air-source heat pumps might be more suitable and cost-effective in warmer areas.
Home Insulation and energy efficiency
A well-insulated and energy-efficient home is critical to maximizing the benefits of a heat pump. Good insulation reduces heat loss during winter and heat gain during summer, allowing the heat pump to work more efficiently.
Before installing a heat pump, it’s essential to evaluate the insulation in your walls, attic, and floors and the efficiency of your windows and doors.
Investing in better insulation and energy-efficient upgrades will improve your heat pump’s performance and lower your overall energy consumption and costs.
Sizing your heat pump
Proper heat pump sizing is crucial for optimal performance, comfort, and energy savings. A heat pump that is too small may struggle to maintain comfortable temperatures, while an oversized unit can lead to short cycling, reduced efficiency, and increased wear and tear.
To determine the right size for your heat pump, a professional installer will typically perform a load calculation, considering factors such as the size and layout of your home, insulation levels, window types, and local climate conditions.
Choosing a heat pump that is correctly sized for your home allows you to enjoy consistent comfort, energy efficiency, and a longer system lifespan.

Selecting the Right Heat Pump
Once you have assessed your home’s needs and requirements, the next step is choosing the type of heat pump that best suits your situation. Several types of heat pumps are available, each with advantages and limitations. In this section, we’ll discuss air sources, ground sources, water sources, and hybrid heat pumps to help you make an informed decision.
Air source heat pumps
Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) are the most common type of heat pump and work by extracting heat from the outdoor air. They are relatively easy to install and suitable for various climates.
However, their efficiency may decrease in freezing temperatures. ASHPs are generally more affordable than other types of heat pumps, making them an attractive option for homeowners seeking cost-effective and eco-friendly heating and cooling solutions.
Ground source heat pumps
Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs), also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilize the ground’s or groundwater’s stable temperatures to provide heating and cooling. While more expensive to install than ASHPs, they offer higher efficiency and are unaffected by outdoor air temperatures.
GSHPs are an excellent choice for homeowners who prioritize long-term energy savings and are willing to invest in a more complex installation process. Their longevity and consistent performance make them a popular option in colder climates.
Water source heat pumps
Water source heat pumps use a body of water, such as a pond or lake, as a heat exchange medium. These systems are less common than air-source and ground-source heat pumps but can provide efficient heating and cooling in suitable locations.
If your property has access to a water source with stable temperatures, a water source heat pump may be a viable option. However, it’s essential to consider factors such as local regulations and the potential environmental impact of the installation.
Hybrid heat pumps
Hybrid heat pumps combine the features of air source and ground source systems, offering enhanced efficiency and versatility. They can automatically switch between different heat exchange sources depending on the outdoor conditions, maximizing energy savings.
Hybrid heat pumps may suit homeowners looking for a more adaptable solution that utilizes air-source and ground-source heat pump technology. However, the initial investment for a hybrid heat pump system can be higher than that of a single-source approach.
Selecting the right heat pump for your home is crucial for optimizing comfort, efficiency, and cost savings. By considering the various types of heat pumps available and evaluating their suitability for your specific needs and climate, you can make an informed decision that will benefit your home for years.
Heat Pump Components
A heat pump system comprises several components that work together to provide efficient heating and cooling for your home. Understanding the role of each component can help you gain a better grasp of how heat pumps operate and maintain the system effectively.
Indoor units
The indoor unit of a heat pump system consists of the evaporator and the air handler. The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the indoor air in cooling mode or releasing heat into the indoor air in heating mode.
The air handler is an essential part of the indoor unit that circulates conditioned air throughout your home. It contains a blower, a filter, and sometimes auxiliary heating elements for supplemental heat during freezing weather.
Outdoor units
The outdoor unit houses the compressor and the condenser. The compressor is a crucial component that increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, enabling it to absorb or release heat more effectively.
The condenser is responsible for releasing heat into the outdoor air in cooling mode or absorbing heat from the outdoor air in heating mode. The outdoor unit also typically contains a fan that helps dissipate heat during condensation.
Refrigerant lines
Refrigerant lines connect a heat pump system’s indoor and outdoor units, allowing the refrigerant to circulate between the two. These lines are insulated to prevent heat loss and ensure optimal system efficiency. Regular inspection and maintenance of the refrigerant lines are essential to prevent leaks and maintain the performance of your heat pump.
Thermostats and controls
Thermostats and control systems are responsible for regulating the operation of your heat pump. They monitor the indoor temperature and signal the heat pump to turn on or off as needed to maintain the desired comfort level.
Modern thermostats often include advanced features, such as programmable schedules, remote access, and compatibility with smart home systems, allowing you to optimize energy savings and enhance the convenience of your heat pump system.
Understanding the components of a heat pump system is essential for homeowners considering heat pump installation or those looking to maintain their existing system effectively.
By familiarizing yourself with the role of each component, you can better appreciate the technology behind heat pumps and ensure the long-term efficiency and reliability of your heating and cooling solution.
Installation Process
Properly installing a heat pump ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity. Hiring a professional installer with experience in heat pump systems is highly recommended to carry out the installation process.
In this section, we will discuss the main steps involved in the installation process, including site preparation, installation of indoor and outdoor units, the connection of refrigerant lines, electrical wiring and controls, and system testing and commissioning.
Site preparation
The first step in the installation process is preparing the site for indoor and outdoor units. This may involve clearing obstructions, leveling the ground, and creating a solid base for the outdoor unit.
For the indoor unit, it’s essential to ensure adequate space for the air handler and easy access for maintenance. Proper placement of both units is crucial for efficient operation and to minimize noise and vibration.
Installation of indoor and outdoor units
Once the site is prepared, the installer will mount the indoor unit, usually on a wall or suspended from the ceiling, depending on the type and model of the heat pump.
The outdoor unit should be positioned on a level surface, with sufficient clearance around it to allow for proper airflow and easy access for maintenance. Ensuring that both units are securely fastened and adequately aligned is vital.
Connection of refrigerant lines
After installing the indoor and outdoor units, the installer will connect the refrigerant lines. These lines are insulated to prevent heat loss and should be routed most efficiently and unobtrusively possible.
The installer will then evacuate the refrigerant lines to remove any air or moisture and charge the system with the appropriate type and amount of refrigerant.
Electrical wiring and controls
The installer will connect the electrical wiring between the indoor and outdoor units and any required connections to the thermostat or control system. Proper electrical connections are essential for your heat pump system’s safe and efficient operation.
The installer should follow all local electrical codes and manufacturer guidelines to ensure a safe and reliable installation.
System testing and commissioning
Once all components are installed, connected, and charged, the installer will test the heat pump system to ensure it operates correctly. This may involve checking for refrigerant leaks, verifying proper airflow, and ensuring that the thermostat and controls function as intended.
The installer will commission the system, adjusting settings to optimize performance and efficiency. Finally, they will provide an overview of the system’s operation and maintenance requirements.
The installation process of a heat pump is a critical factor in the system’s overall performance and lifespan. By hiring a professional installer and understanding the main steps involved, you can ensure that your heat pump is installed correctly, providing you with efficient and reliable heating and cooling for years.
Hiring a Professional Installer
Proper heat pump system installation ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity. Hiring a professional installer with experience in heat pump systems is highly recommended to ensure a smooth installation process and avoid potential issues.
In this block, we’ll discuss finding a reputable installer, evaluating their credentials and experience, and obtaining quotes to compare costs.
Finding a reputable installer
To find a reputable heat pump installer, ask for recommendations from friends, neighbors, or colleagues who installed heat pumps in their homes. Local HVAC associations and online directories can also be valuable resources for identifying professional installers in your area.
Online reviews and testimonials can provide insights into the quality of work and customer satisfaction levels of potential installers.
To find Heat Pump Professional Installer Near Me, enter this term in the search box below
Evaluating credentials and experience
Before hiring a heat pump installer, evaluating their credentials and experience is essential. Verify that the installer is licensed and insured. Check for any certifications they may hold, such as NATE (North American Technician Excellence), demonstrating a high level of expertise in HVAC systems.
Ask about their experience with heat pump installations, particularly with the specific type and brand of heat pump you are considering. Request references from previous customers and follow up to inquire about the quality of work, communication, and overall satisfaction with the installation process.
Obtaining quotes and comparing costs
Once you have identified a few potential installers, request detailed quotes to install your heat pump system. These quotes should include a breakdown of costs for equipment, labor, permits, and any additional services that may be required, such as ductwork modifications or electrical upgrades.
Comparing quotes from multiple installers can help you identify the best value for your investment. However, it’s important not to base your decision solely on price. Consider the installer’s experience, credentials, reputation, and the quality of the equipment and materials they propose to use.
Hiring a professional installer for your heat pump system is crucial to ensure a successful installation and long-term performance. By finding a reputable installer, evaluating their credentials and experience, and comparing quotes, you can make an informed decision that will benefit your home and your comfort.
DIY Heat Pump Installation
While hiring a professional installer is recommended for most homeowners, some may consider taking on the challenge of a DIY heat pump installation.
If you’re contemplating this option, it’s crucial to assess your skills and tools, understand permits and regulations, and know the installation steps and precautions involved.
Assessing your skills and tools
Before embarking on a DIY heat pump installation, evaluate your skills, knowledge, and experience with HVAC systems and electrical work. Installing a heat pump requires a solid understanding of heating and cooling principles and proficiency in electrical wiring, plumbing, and ductwork.
Additionally, you’ll need access to specialized tools and equipment, such as vacuum pumps, refrigerant gauges, and pipe benders. If you’re unsure about your ability to handle these aspects, hiring a professional installer is the safer and more reliable option.
Permits and regulations
Installing a heat pump may require permits and compliance with local building codes and regulations. It’s essential to research and obtain any necessary permits before starting your DIY installation project.
Failing to comply with local codes and regulations can result in fines, increased insurance rates, or even the need to uninstall and reinstall the system with a professional.
Also, be aware that some manufacturers may void the warranty if a licensed professional does not install the heat pump.
Installation steps and precautions
If you decide to proceed with a DIY heat pump installation, familiarize yourself with the installation steps and precautions outlined in the manufacturer’s manual.
These steps typically include site preparation, indoor and outdoor unit installation, refrigerant line connections, electrical wiring, and system testing. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure a safe and proper installation.
It’s crucial to recognize the risks associated with DIY heat pump installation, including potential injury, damage to your home, or improper installation that could compromise the system’s efficiency and lifespan.
If you’re uncertain about any installation process, consult a professional installer for guidance or consider hiring a professional to complete the project. DIY heat pump installation can be a rewarding challenge for experienced homeowners.
Still, it’s essential to approach the project with caution and a thorough understanding of the skills and knowledge required.
Cost Analysis
When considering a heat pump installation, it’s essential to analyze the costs involved, including upfront costs, operational costs, and potential incentives and rebates. This section will discuss the factors contributing to these costs and how they can impact your decision to install a heat pump system.
Upfront costs and factors
The upfront cost of a heat pump installation includes the system’s price, labor, permits, and any additional equipment or modifications needed.
Factors that can affect the upfront cost include the type and brand of heat pump, the size and complexity of the installation, and local labor rates.
While heat pumps can be more expensive upfront than traditional heating and cooling systems, but their efficiency and long-term energy savings can offset the initial investment.
Operational costs and savings
Heat pumps offer significant operational cost savings compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, as they transfer heat rather than generate it. This results in lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
Operational costs will vary depending on factors such as local climate, energy rates, and system efficiency. It’s essential to consider these factors when evaluating the long-term cost-effectiveness of a heat pump installation.
Proper maintenance and periodic servicing can also help to minimize operational costs and ensure optimal system performance.
Incentives and rebates
Various federal, state, and local incentives and rebates may be available to help offset the upfront cost of a heat pump installation. These programs can include tax credits, utility rebates, or low-interest financing options.
To maximize the financial benefits of a heat pump installation, research the incentives and rebates available in your area and consult with your installer to ensure your system meets the eligibility requirements.
These programs can significantly reduce the initial investment and make the heat pump installation more affordable.
A thorough cost analysis can help you decide whether a heat pump installation is the right choice for your home. By considering upfront costs, operational savings, and available incentives and rebates, you can determine if a heat pump system is a cost-effective solution for your heating and cooling needs.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are essential to ensure your heat pump system’s efficient operation and longevity. In this section, we’ll discuss routine maintenance tasks, common issues, and their solutions, and when to call a professional.
Routine maintenance tasks
Regular maintenance of your heat pump system is crucial to maintain its performance and efficiency. Routine maintenance tasks include cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting and cleaning indoor and outdoor coils, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring proper airflow around the indoor and outdoor units.
Most of these tasks can be performed by homeowners, while others, such as checking refrigerant levels or servicing the compressor, should be handled by a professional technician during periodic servicing.
Common issues and solutions
Despite regular maintenance, heat pump systems may occasionally encounter issues that require troubleshooting. Some common problems include reduced heating or cooling output, unusual noises, or the system’s malfunction.
These issues can be resolved in many cases by checking for and addressing simple causes, such as dirty filters, blocked airflow, or tripped circuit breakers. However, more complex problems, such as refrigerant leaks or compressor issues, will require professional attention.
When to call a professional
While many heat pump maintenance tasks and troubleshooting can be performed by homeowners, it’s important to know when to call a professional.
If you encounter an issue that you cannot resolve on your own or if you suspect a more significant problem, such as a refrigerant leak or compressor failure, it’s best to consult a professional technician.
Regular professional servicing, typically once or twice a year, can help identify and address potential issues before they become more costly or cause damage to your system.
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for your heat pump system’s long-term performance and reliability. By performing routine maintenance tasks and knowing when to call a professional, you can ensure that your heat pump continues to provide efficient heating and cooling for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions
As you consider a heat pump installation for your home, you may have questions about the process, costs, and benefits. In this section, we’ll address some frequently asked questions related to heat pump installations.
How much does a heat pump installation cost?
The cost of a heat pump installation can vary widely depending on factors such as the type and brand of heat pump, the size and complexity of the installation, and local labor rates.
On average, a heat pump installation can range from $4,000 to $10,000 or more, including the cost of the heat pump itself, labor, permits, and any additional equipment or modifications needed.
How long does it take to install a heat pump?
The duration of a heat pump installation can vary depending on the project’s complexity and your home’s specific requirements.
Generally, a heat pump installation can take anywhere from one to three days, with more complex installations potentially taking longer.
Can I install a heat pump myself?
While some experienced homeowners may choose to tackle a DIY heat pump installation, hiring a professional installer is generally recommended.
Heat pump installations require specialized tools, knowledge, and experience in HVAC systems, electrical work, and plumbing.
Also, improper installation can reduce efficiency, decrease system lifespan, and voided warranties.
Hiring a professional installer is the safer and more reliable option unless you have the necessary skills and expertise.
How energy efficient are heat pumps?
Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient heating and cooling systems that can significantly save energy costs compared to traditional furnaces and air conditioners.
The efficiency of a heat pump is measured by its coefficient of performance (COP) or heating seasonal performance factor (HSPF) for heating and its seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) for cooling.
A higher COP, HSPF, or SEER rating indicates greater energy efficiency.
What size heat pump do I need for my home?
The heat pump size you need for your home depends on factors such as your home’s size, insulation, climate, and desired indoor temperature. An appropriately sized heat pump will operate efficiently and provide consistent heating and cooling.
A professional installer or HVAC technician can help you determine the correct size heat pump for your specific needs by performing a load calculation that considers these factors.
As you explore the option of installing a heat pump in your home, these answers to frequently asked questions can help you make an informed decision about whether a heat pump system is the right choice for your heating and cooling needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, modern heat pump systems have revolutionized how we maintain a comfortable living space, offering a cost-effective and energy-efficient alternative to traditional furnaces and air conditioning units.
By considering factors such as heat pump costs, heat pump installation costs, and the various types available – including air source heat pumps, geothermal heat pumps, and solar heat pumps – homeowners can make an informed decision on the most suitable system for their needs.
Compared to conventional systems like gas furnaces and electric furnaces, heat pumps provide both cool air and warm air with greater efficiency, resulting in significant energy bill savings.
Furthermore, the installation of outdoor and indoor units, such as mini split heat pump units, can be tailored to the unique requirements of any home, regardless of size or climate.
In addition, modern heat pumps can be combined with renewable energy sources like solar panels, further reducing utility costs and environmental impact.
With professional installation and maintenance, new heat pump systems can last for many years, providing consistent heating and cooling while minimizing the need for repairs.
Investing in a heat pump system can save money in the long run, improve home comfort, and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels like oil, natural gas, and propane.
As we move towards a more sustainable and energy-conscious future, heat pumps play a crucial role in reducing our carbon footprint and making our homes more eco-friendly.
Ultimately, the decision to switch to a heat pump system should be based on thorough research and consultation with HVAC professionals.
By understanding the various factors that affect heat pump costs, installation fees, and maintenance requirements, homeowners can make the best choice for their budget and comfort.
With proper planning and expert guidance, the transition to a heat pump system can be a rewarding investment in the long run, resulting in a comfortable, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly home.
Last update on 2024-07-26 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API





























