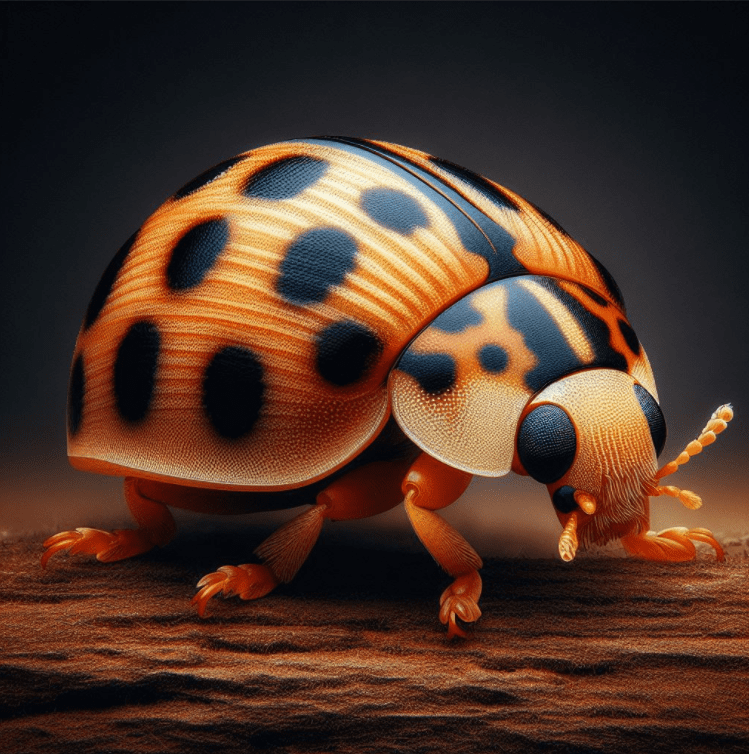

Imagine the excitement of growing those beautiful heirloom beans you’ve been dreaming of. But the Mexican bean beetle threatens to destroy your hard work! These pests can rapidly defoliate your plants, leaving you with empty pods and disappointment. Discover the organic strategies to reclaim your garden and enjoy a bountiful heirloom bean harvest.
How to Identify Mexican Bean Beetles
Description
The Mexican bean beetle may resemble a harmless ladybug, but its appetite for bean foliage makes it a formidable garden foe. Both adults and larvae feast on leaves, flowers, and pods. Adult beetles are copper-colored with 16 black spots, while the larvae are yellow and spiky.
Life Cycle
Understanding the Mexican bean beetle’s life cycle is crucial for effective control:
- Eggs: Females lay clusters of yellow eggs on the undersides of bean leaves.
- Larvae: After hatching, larvae go through several stages, their destructive potential growing with each molt.
- Pupae: Larvae transform into pupae, still attached to the leaves.
- Adults: New adult beetles emerge, ready to continue the feeding and reproduction cycle.
Prevention is Key: Cultural Practices Against Mexican Bean Beetles
Crop Rotation
Rotate your bean planting location each year. This disrupts the beetle’s life cycle, preventing populations from building up in the same spot.
Sanitation
Cleanliness is crucial! Remove plant debris at the end of the season, depriving beetles of overwintering sites.
Companion Planting

Harness the power of plant partnerships:
-
Strong-scented Herbs:
- Dill: Confuses pests and attracts beneficial insects.
- Cilantro: Repels many pests, including bean beetles.
- Garlic: Its pungent scent repels a wide range of insects.
- Chives: Similar deterrent effect to garlic.
-
Flower Power:
- Marigolds: Their scent is strongly disliked by bean beetles.
- Nasturtiums: Act as trap crops, luring beetles away from your beans.
- Zinnia: Attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings.
-
Additional Options:
- Tansy: Repels a variety of pests.
- Summer Savory: Deters bean beetles.
- Catnip: Although cats love it, many pests avoid its scent.
Important Note: Remember to interplant them directly amongst your bean crops for maximum effectiveness when using companion plants.
Physical Controls for Direct Intervention
Floating Row Covers
Lightweight, breathable fabrics like row covers create a physical barrier between your beans and the beetles. Remember to remove them during flowering to allow for pollination.
Hand-picking
This time-tested method is highly effective. Regularly inspect your plants and remove adults, larvae, and egg clusters. Dispose of them in soapy water.
Natural Predators: Biological Control for Mexican Bean Beetles
Beneficial Insects
Welcome these natural predators to your garden:
- Ladybugs: Both adults and larvae devour bean beetle eggs and young larvae.
- Lacewings: Their larvae are voracious feeders, targeting many garden pests.
- Parasitic Wasps lay their eggs within beetle larvae, eventually killing them.
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) var. tenebrionis
This naturally occurring bacterium specifically targets beetle larvae. It’s harmless to humans, pets, and beneficial insects.
Organic Pesticides – Use Sparingly
After implementing preventative and biological control methods, organic pesticides should be considered a last resort. However, there are situations where they can be a necessary tool to protect your heirloom bean crop.
Here are some key factors to consider:
- Severity of Infestation: If your bean plants are heavily infested with Mexican bean beetles despite other control methods, organic pesticides might be needed to prevent significant damage or crop loss.
- Life Stage of the Pest: Organic pesticides like Neem oil are most effective against larvae. Consider hand-picking or using physical barriers like row covers if your primary concern is adult beetles.
- Timing and Weather Conditions: Always follow application instructions carefully, paying close attention to recommended timing and weather conditions. Rain can wash away the product, reducing its effectiveness.
Essential Considerations Before Using Organic Pesticides:
- Selectivity: Choose organic pesticides that target Mexican bean beetles specifically, minimizing harm to beneficial insects and other garden creatures.
- Spot Treatment: Opt for spot treatment whenever possible instead of spraying the entire plant. This minimizes exposure and protects beneficial insects hiding on other parts of the plant.
- Organic Doesn’t Mean Completely Safe: While organic pesticides are generally less toxic than synthetic options, always read and follow label instructions carefully. Wear protective gear like gloves and a mask if recommended.
- Develop Resistance: Overreliance on the same organic pesticide can lead to pest resistance. Rotate organic options or combine them with other control methods for long-term effectiveness.
Remember: Prevention is always the best strategy. Focus on cultural practices, companion planting, and encouraging beneficial insects to create a healthy garden ecosystem that discourages pest problems. But when necessary, organic pesticides can be a valuable tool in your organic Mexican bean beetle control toolbox.
Companion Plants to Help Prevent Bean Rust
Bean rust, a fungal disease, is another potential problem. Protect your plants with:
- Garlic, Onions, and Chives: Their pungent scent repels insects that can spread the rust fungus.
Putting It All Together with Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a strategic approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention and long-term solutions. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on chemical pesticides, IPM focuses on a combination of tactics to manage pest populations below damaging levels while minimizing risks to human health and the environment.
Here’s a breakdown of how IPM works in your garden:
1. Monitoring and Scouting:
- Regularly inspect your bean plants for signs of Mexican bean beetle activity. Look for adult beetles, larvae, eggs, and leaf damage.
- Monitor for the presence of beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings.
2. Setting Action Thresholds:
- Determine the level of pest infestation that warrants intervention. This helps you avoid unnecessary control measures. For example, hand-picking might suffice if you see a few solitary beetles. However a large population might require a combination of methods.
3. Applying a Multi-Pronged Approach:
IPM integrates various non-chemical and chemical controls, depending on the situation. Here’s how the methods we discussed earlier fit into the IPM framework:
- Prevention: Crop rotation, sanitation, companion planting with beneficial herbs, and installing row covers all play a crucial role in preventing infestations.
- Monitoring and Scouting: As mentioned earlier, consistent monitoring allows for early detection and intervention.
- Biological Control: Introducing or encouraging beneficial insect populations helps create a natural balance in your garden. Applying Bt var. tenebrionis can also be part of this strategy.
- Physical Controls: Hand-picking can be highly adequate for small infestations. Row covers offer physical protection.
- Organic Pesticides (as a last resort): If other methods prove insufficient, consider organic options like neem oil or pyrethrin cautiously and only when necessary.
Benefits of Using IPM:
- Reduced Reliance on Chemicals: This protects your health, your family’s health, and the environment.
- Sustainable Pest Control: IPM encourages long-term solutions and helps prevent pest resistance to specific pesticides.
- Healthy Garden Ecosystem: You create a balanced and resilient garden by promoting biodiversity with beneficial insects and companion plants.
Remember:
- The specific control methods used in your IPM plan will depend on the severity of the infestation and your personal preferences.
- Consistency is key! Regularly monitor your plants and be prepared to adjust your strategy as needed.
By following these principles, you can effectively manage Mexican bean beetles and other pests using an organic IPM approach, ensuring the health and productivity of your precious heirloom bean crop.
Monitoring is Essential
Regularly scout your bean plants for the first signs of beetle activity. Early intervention is critical!
Conclusion
By embracing organic Mexican bean beetle control, you protect your heirloom beans, the environment, and yourself. Enjoy the fruits of your labor with a delicious, healthy, and truly sustainable harvest.






















